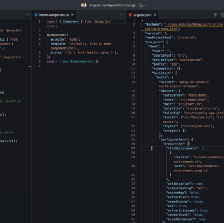
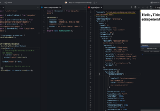
Here is the following code to get the example that how you can spy an observable.
api.service.ts
getUserDetails(id: string) : Obervable<UserDetails> {
let url = `${this.apiService.getUserDetailsUrl()}/${id}`;
return this.http.get<UserDetails>(url, headers: {‘Content-type’: ‘application/json’});
}
user.component.ts
export class UserComponent implements OnInit{
let userData;
constructor(private apiSrv: ApiService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.getDetails(id);
}
getDetails(id: string) {
this.apiSrv.getUserDetails(id).pipe(takeUtil(this.destroy$))
.subscribe(data => {
this.userData = data.details;
});
}
}
user.component.spec.ts
import { TestBed, CompponentFixture } from ‘@angular/core/testing’;
import { HttpClientTestingModule, HttpTestingController} from ‘@angular/common/http/testing’;
import { ApiService } from ‘../core/api.service’;
describe(‘UserComponent’, () => {
let component: UserComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture< UserComponent>;
let userRes = {
result: {
id: ‘u1343124’,
name: ‘test’,
type: ‘lite’,
joined: ‘’
}
};
beforeEach(async(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
import: [HttpClientTestingModule],
declarations: [UserComponent],
providers: [ApiService]
});
apiService = TestBed.inject(ApiService);
spyOn(apiService, ‘getUserDetails’).and.returnValue(of(userRes));
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(UserComponent);
fixture.detectChanges();
}));
it(‘should be create’, () => {
expect(service).toBeTruthy();
)};
)};